This module is in Beta. Please confirm all outputs with alternative methods.
Introduction
The 'Rainfall Analyser' form is used to import, interrogate, interpolate, extrapolate and export rainfall information. The 'Rainfall Analyser' form incorporates four tabs:
4.Settings
A detailed description of the contents of each tab is provided below.
The data generated by the Rainfall Analyser can also be used to develop rainfall isohyet maps and animations within the main CatchmentSIM window.
The 'Source Rainfall' tab is shown below and is used to:
•import rainfall data files;
•summarise key information for each gauge;
•visualise the raw data; and,
•review the raw data to identify when significant rainfall events have occurred.
Importing Rainfall Files
To start using the rainfall analyser, raw rainfall data must be imported for one or more gauges. To import rainfall data select the  button. A range of rainfall file formats are currently supported including:
button. A range of rainfall file formats are currently supported including:
•Bureau of Meteorology (BoM) rainfall files (6 minute, 30 minute and daily) - daily BoM data can be automatically downloaded and imported into the Rainfall Analyser using the 'Find Nearby Gauges' dialog.
•Manly Hydraulics Laboratory (MHL) CSV files
•Mean Daily Rain Gauge Precipitation 5km Grids (*.nc)
•Generic CSV format
Limiting Imported Data Range
If you are only interested in importing rainfall data across a specific time period, the 'Limit Range' check box can be selected. This will enable you to select a start and end date for the imported data. When activated, the 'Limit Range' option can significantly increase the speed of the rainfall data import and subsequent data processing and will also reduce the hard disk space consumed by the resulting CatchmentSIM project.

Deleting Rainfall Gauges
To remove any rainfall gauges and associated data from the project, ensure the gauge(s) to be removed have a "check" next to them in the left most column of the 'Time Series Summary' Table. To select or unselect all gauges in the table, right click on the left column in the table and select 'Select All' or 'Unselect All' from the popup menu. Once all of the desired gauges are checked, select  .
.
To review the raw rainfall data, select the desired gauge in the 'Time Series Summary Table' and ensure the 'Raw Data' tab is active near the bottom of the page. The raw rainfall data for the selected gauge will be displayed in the chart on the lower left of the dialog and will also be displayed in tabular format:
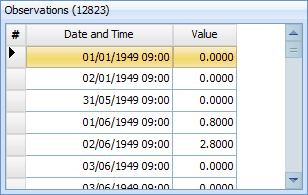
The raw data can be exported to CSV file by selecting the  button.
button.
Identifying Significant Historic Rainfall Events
It is often necessary to select one or more discrete historic rainfall events for the purposes of calibrating a hydrologic model or simulating a specific historic event. The 'Potential Events' tab can be used to assist in the selection of significant historic rainfall events. To use the 'Potential Events' feature, it is first necessary to select an appropriate gauge for the analysis. This gauge should ideally have a long record (refer start and end dates in the 'Time Series Summary Table') and be located within or in close proximity to the catchment of interest.
Now a 'critical duration' must be specified. CatchmentSIM will search through the rainfall data for the largest accumulated rainfall depths that have occurred over this selected duration. Therefore, it is important that the duration is long enough to fully contain most historic events. A 1 day duration is typically a good place to start as it will typically make all rainfall gauges available and will contain most significant historic events.
You will also need to define how many historic events you wish to search for. For example, if '10' events are defined, the Rainfall Analyser will search for the 10 largest accumulated rainfall depths.
Once the three inputs are defined, press the  button. The program will search for the largest accumulated rainfall depths over the selected duration for the selected gauge and will display the results in tabular format, as shown below. The program will also summarise the accumulated rainfall depths that occurred before and after the main rainfall burst.
button. The program will search for the largest accumulated rainfall depths over the selected duration for the selected gauge and will display the results in tabular format, as shown below. The program will also summarise the accumulated rainfall depths that occurred before and after the main rainfall burst.
The right side of the 'Potential Events' tab can also be used to automate the setup of an historic rainfall event (normally completed on the 'Rainfall Events' tab). To setup an historic rainfall event, select the appropriate event from the table. The 'Start Date' and 'End Date' will update to reflect the selected event. Note that the program will default to a start date one 'duration' before the main burst and will default to an end date one 'duration' after the main rainfall burst. However, the default start/end dates and time can be modified, if desired. Once the start and end date/time are defined, press the  button. The start and end date/time will be transferred to the 'Rainfall Events' tab where a new rainfall event will be automatically created. Further information on the 'Rainfall Events' tab is provided below.
button. The start and end date/time will be transferred to the 'Rainfall Events' tab where a new rainfall event will be automatically created. Further information on the 'Rainfall Events' tab is provided below.
The 'Rainfall Events' tab is shown below and is used to:
•Define an historic rainfall event including start/end dates and times, time step and spatial interpolation approach
•Specify which rain gauge(s) will be used to define the historic event
•Define how gauge data will be down-sampled/interpolated (if necessary)
•Export interpolated rainfall data for each gauge
•View pluviographs and cumulative rainfall charts for each gauge
To create new rainfall event, click the  button. A new 'Add Event' dialog will appears, similar to that shown below:
button. A new 'Add Event' dialog will appears, similar to that shown below:
The 'Add Event' dialog requires the following information to be defined:
•Event Name: Name of the historic event (e.g., June 1986 Flood)
•Start Date/Time: the start date and time for the historic event. Care should be taken in defining the start time, particularly when using daily rainfall data. Daily rainfall totals are typically read at 9am each day. Therefore, a start time of 9:00am would be appropriate to ensure daily rainfall totals are conserved across the event.
•End Date/Time: the end date and time for the historic event. As with the start time, care should be taken when selecting an appropriate end time. If daily gauge data is being used, an end time of 9:00am is recommended.
•Time Step: defines the temporal resolution for the event. All gauge data will be re-sampled or accumulated from the native time step of the gauge data to this time step. The time step must be equal to or larger than the smallest time step of the raw gauge data.
•Spatial Interpolation Method: Defines how rainfall will be spatially interpolated between gauge locations. Four interpolation methods are available: Inverse Distance Weighted, Thiessen Polygon, Natural Neighbor and Kriging (Ordinary).
Once each of the above inputs is defined, the rainfall event can be accepted by selecting the  button. Alternatively, the creation of the new rainfall event can be cancelled by selecting the
button. Alternatively, the creation of the new rainfall event can be cancelled by selecting the  button.
button.
The event can be modified at a later date by highlighting the appropriate event on the 'Events Summary Table' and selecting the  button.
button.
Assigning Gauges to a Rainfall Event
Once a new rainfall event has been created, the 'Rainfall Analyser' will search through all gauges on the 'Source Rainfall' tab to determine which gauges were active between the event start and end dates/times. Those gauges will be displayed in the 'Assigned Source Time Series' table. The table will also display the total rainfall depth for the event at each gauge, the number of rainfall observations during the event as well as the temporal resolution of the raw data.
If additional gauges are added to the 'Source Rainfall' tab after a rainfall event is defined, they will not be automatically added to the event. To search for and add any new gauges to an existing event, click the  button.
button.
The temporal availability of rainfall data for each gauge during the nominated event can be charted by selecting  . This enables any potential data gaps to be identified.
. This enables any potential data gaps to be identified.
Once the gauge data has been reviewed, those gauges which are considered to comprise valid data need to "assigned" to the historic event. To assign gauges to the event, ensure the check box in the left column of the 'Assigned Source Time Series' table is checked for all required gauges (all gauges will be checked by default) and then press the  button.
button.
To remove an assigned gauge from a rainfall event, ensure the check box next to the gauge is checked and then select the  button.
button.
All available rain gauges will be displayed within the 'Assigned Source Time Series' table. However, only those gauges that have been assigned to the event (highlighted in green below) will be used in the rainfall event calculations. Unassigned gauges will be highlighted in yellow.
Defining a Temporal Interpolation Approach
If the event time step is less than the temporal resolution of any of the raw gauge data, it will be necessary to down-sample/interpolate this raw gauge data. Three different temporal interpolation approaches are available:
•Linear: subdivides the rainfall equally over each time step. For example, if a 1 hour time step was selected, any daily rainfall depths would be subdivided to provide 24 equal hourly rainfall depths.
•CSV Temporal Pattern: defines the temporal variation based upon a CSV file. The CSV file should contain a single column of decimal value for each time step. The decimal value should sum to 1 to ensure the total rainfall depth is conserved across the event. For example, if a 24 hour event is defined with a 1 hour time step, 24 rows of data would need to be provided. The sum of the 24 values will need to equal 1.
•Nearest Gauge: defines the temporal variation in rainfall based upon the closest gauge with a temporal resolution equal to or smaller than the adopted time step. If only one such gauge is available, all gauges will employ the same temporal pattern. If more than one such gauge is available, the straight line distance between the gauges is used to determine which gauge is nearer.
Different temporal interpolation approaches can be applied to individual gauges. Alternatively, a CSV temporal pattern or nearest gauge can be globally assigned to all appropriate gauges by selecting the appropriate option from the drop down menu of the  button.
button.
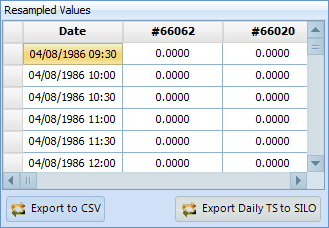
Once all gauges have been re-sampled to the selected event time step, the re-sampled data can be viewed in the 'Resampled Value' table. The re-sampled data can also be exported to CSV:
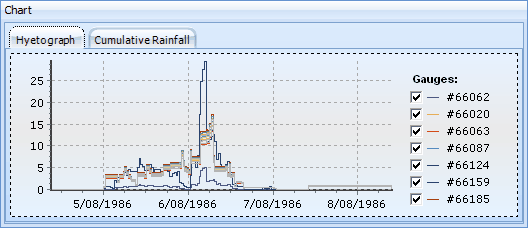
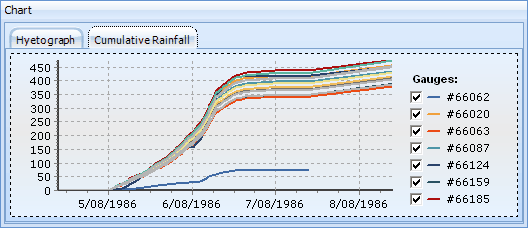
The re-sampled rainfall data can also be reviewed in the form of a rainfall hyetograph or cumulative rainfall chart by selecting the appropriate chart tab:
The 'Subcatchment Rainfall' tab is shown below and is used to calculate unique rainfall time series for each subcatchment (or external GIS polygon / grid layer) based upon the spatially and temporally interpolated rainfall values defined on the 'Rainfall Events' tab.
Subcatchment Weighted Rainfall
To calculate rainfall time series for each subcatchment in the CatchmentSIM project, select the desired event from the drop down menu on the top left of the 'Subcatchment Rainfall' tab and click the  button. CatchmentSIM will calculate a weighted average rainfall depth for each subcatchment for each time step based on consideration of rainfall depths across all DEM grid cells within the subcatchment (the rainfall depths for each grid cell are interpolated for each time step using the spatial interpolation approach defined on the 'Rainfall Events' tab).
button. CatchmentSIM will calculate a weighted average rainfall depth for each subcatchment for each time step based on consideration of rainfall depths across all DEM grid cells within the subcatchment (the rainfall depths for each grid cell are interpolated for each time step using the spatial interpolation approach defined on the 'Rainfall Events' tab).
Once the weighted average rainfall depths are calculated for each subcatchment and each time step, they will be displayed in tabular as well as chart form. Each subcatchment is represented as a separate column in the table.
Weighted Rainfall for Other Polygons
Weighted average time series can also be calculated for external grid layers. This can be useful if subcatchment delineation was completed in a third party application. Time series can only be carried out on grid layers, so if the subcatchment delineation is in the format of a vector GIS layer, it will have to be imported into CatchmentSIM and converted to a grid layer using the convert to grid process. This option is available under the Analysis >> Create Grid >> Create Grid from Layer. Once the grid is imported or created, select it from the drop down menu and select the  button. CatchmentSIM will calculate a weighted average rainfall depth for each time step based on consideration of rainfall depths across all grid cells with unique grid values. Similarly to the subcatchment weighted rainfall, the rainfall depths for each grid cell are interpolated for each time step using the spatial interpolation approach defined on the 'Rainfall Events' tab).
button. CatchmentSIM will calculate a weighted average rainfall depth for each time step based on consideration of rainfall depths across all grid cells with unique grid values. Similarly to the subcatchment weighted rainfall, the rainfall depths for each grid cell are interpolated for each time step using the spatial interpolation approach defined on the 'Rainfall Events' tab).
Export to CSV
Once either the 'subcatchment weighted rainfall' or 'grid zone rainfall' has been calculated, the results can be exported to a *.csv file for use in external applications and reporting. Click the  button and simply select a save location.
button and simply select a save location.
The settings tab allows the user to define the number of decimal points that are used for all interpolated and weighted average rainfall values.
Creating Rainfall Isohyet Maps
Once a rainfall event has been defined, it can be used as the basis for developing rainfall isohyet maps/rainfall depth grids within the main CatchmentSIM display. When combined with the 'Time Series Controls' and/or 'Create Animation' dialog, the rainfall isohyet maps can be animated to show how the rainfall varied spatially and temporally during each rainfall event.
To create a rainfall isohyet map, first select the "OK" button to close the Rainfall Analyser.
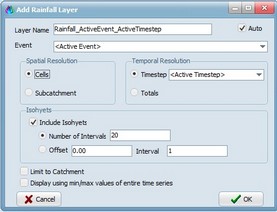
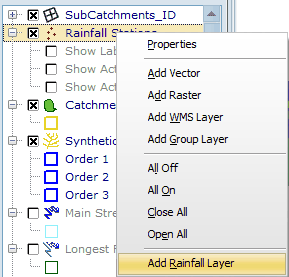
Now right click on the Layer Controller and select "Add Rainfall Layer":
The following window will appear which allows you to define how each rainfall event will be displayed in the main CatchmentSIM window:
The following variables need to be defined:
•Layer Name: Allows the user to specify a name for the new time series layer. This name will appear within the Layer Controller layer list. If the 'Auto' check box is selected, a name will be automatically assigned based on the event name (as defined on the Events tab of the Rainfall Analyser) and the event time step.
•Event: Allows you to select which of the available rainfall events (as as defined on the Events tab of the Rainfall Analyser) will be displayed
•Spatial Resolution:
- Cells: Will calculate a unique rainfall depth for each DEM cell for each time step. The rainfall depths are calculated using the interpolation approach specified on the Events tab.
- Subcatchment: Will calculate a weighted average rainfall depth for each subcatchment.
•Temporal Resolution:
- Timestep: Select <Active Timestep> to retain the defined event time step as part of the animation. If a specific time step is selected, only the total rainfall for that single time step will be displayed.
- Totals: Will produce a rainfall isohyet map with a single time step showing the total depth of rainfall for the entire event.
•Include Isohyets: If selected, it will create a rainfall isohyet layer as a vector layer. The vector layer will display lines of equal rainfall depth (i.e., effectively a rainfall depth contour map)
- Number of Intervals: If selected, allows the user to define the how many contour/isohyet lines will be displayed.
- Offset: If selected, this defines the contour offset relative to the lowest rainfall depth (for example, if the minimum rainfall was 10mm and an offset of 5 was defined, the minimum contour would be 15mm). The 'Interval' is then be used to display the contour increment above this minimum contour.
•Limit to catchment: If selected, the rainfall layer will be clipped to the catchment boundary
•Display using min/max values of entire series: if selected, a constant min/max and isohyet contour interval will be used across all time steps. If not selected, unique min/max and contours will be developed for each time step
Once all of the required information is defined, click the "OK" button. CatchmentSIM will create two new layers and add them to the Layer Controller:
•Rainfall Depth Grid Layer: contains the interpolated rainfall depths for each DEM cell/subcatchment in a raster (i.e., grid) format.
•Isohyet Vector Layer: contains rainfall depth contours in a vector (i.e., SHP) file format.
Once the layers have been created, they can be animated using the Time Series Controls. An animation can also be created and saved to an AVI video file using the 'Create Animation' button.